The ABS light on a car indicates a malfunction within the Anti-lock Braking System, signaling that the safety feature is currently disabled. Common triggers include a failed wheel speed sensor, a defective ABS control module, low brake fluid levels, or a blown fuse. While standard braking usually remains functional, the vehicle will not prevent wheel lockup during emergency stops until the system is repaired.
Seeing a warning light illuminate on your dashboard can be a source of immediate anxiety for any driver. Among the most common yet misunderstood warnings is the “ABS” light. Unlike the Check Engine Light, which often pertains to emissions and engine efficiency, the ABS light is directly tied to the safety dynamics of your vehicle. When the abs light on car dashboards illuminates, it is the vehicle’s computer communicating a specific failure in the traction and braking control network.
In this comprehensive guide, we will dismantle the technical complexities of the Anti-lock Braking System. We will explore why this light turns on, how to interpret the error codes, the difference between a minor sensor glitch and a major module failure, and exactly what steps you need to take to restore your vehicle’s safety features.
What Is the Anti-lock Braking System?
To understand why the light is on, one must first understand what the system does. The Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a safety feature that prevents the wheels from locking up (ceasing rotation) while you are braking. If the wheels lock up, the tires skid across the pavement, causing the driver to lose steering control. ABS automatically modulates the brake pressure—pulsing the brakes hundreds of times per second—to allow the wheels to rotate just enough to maintain traction, thereby enabling the driver to steer around obstacles while braking heavily.
The system relies on a network of sensors, a computer module (ECU), and a hydraulic control unit. When the ignition is turned on, the system performs a self-check. If the computer detects that it is not receiving data from a sensor, or if the hydraulic pump is not responding, it illuminates the ABS light to alert the driver that the system has been deactivated to prevent erratic behavior.
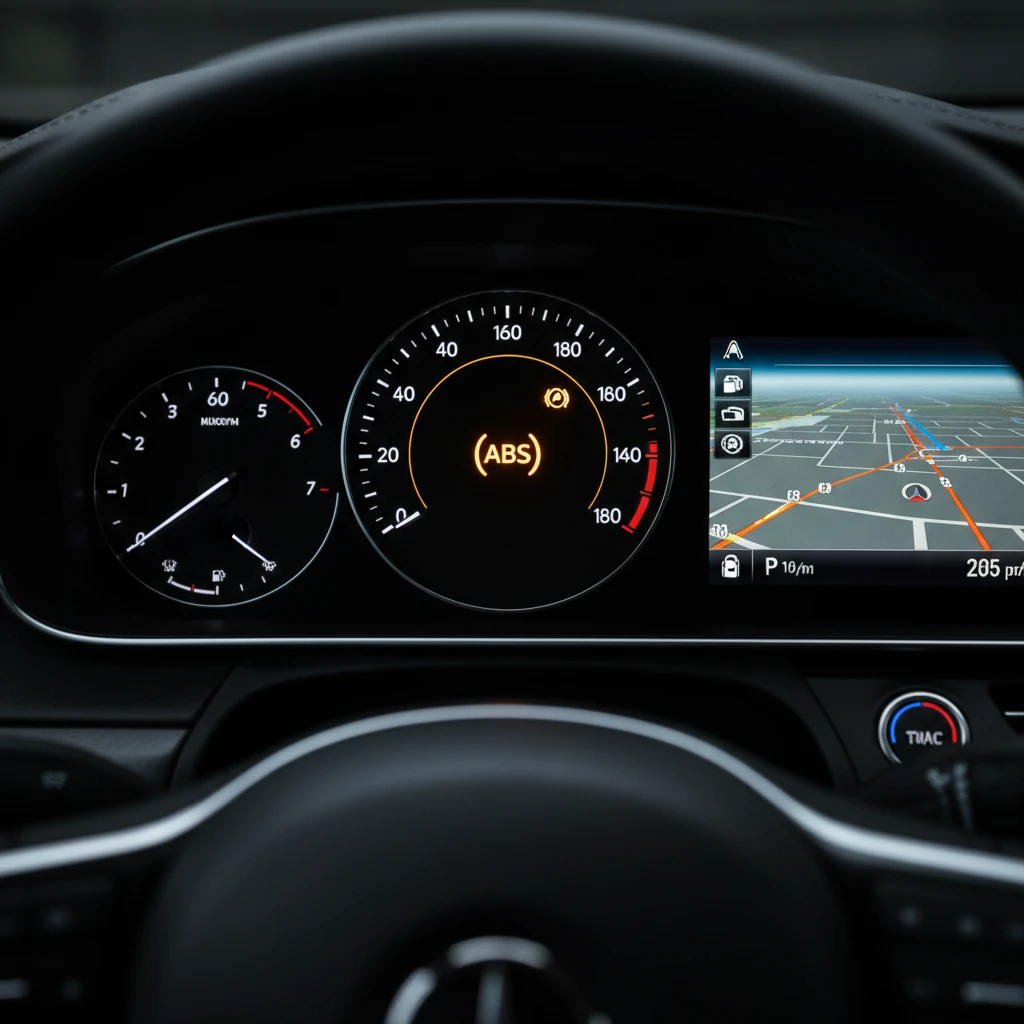

Is It Safe to Drive With the ABS Light On?
This is the most frequent question asked by drivers facing this issue. The short answer is: Yes, but with significant caveats.
When the ABS light is on, your car’s conventional braking system generally remains fully operational. You will still be able to slow down and stop the vehicle using the hydraulic brakes. However, the anti-lock feature is suspended. This means that if you panic-stop or brake hard on a wet, icy, or gravel surface, your wheels may lock up, leading to a skid and a potential loss of steering control.
Furthermore, many modern vehicles integrate the ABS with other stability systems, such as Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control Systems (TCS). Often, when the ABS fails, these associated systems are also disabled. If you must drive with the light on, drive cautiously, increase your following distance, and avoid aggressive braking. If the red “BRAKE” light comes on alongside the amber ABS light, this indicates a serious hydraulic failure (such as severe fluid loss), and the car should not be driven.
Common Causes for the ABS Light on Car
The ABS system is sensitive. It requires precise data to operate. When that data stream is interrupted, the light triggers. Below are the most frequent culprits found during diagnostics.
1. Blown Fuse
Like all electrical components in a vehicle, the ABS system is protected by fuses. A power surge or short circuit can blow the fuse, cutting power to the ABS computer or pump. This is the simplest and cheapest fix, though often overlooked.
2. Low Brake Fluid
The ABS system shares hydraulic fluid with the main braking system. If the fluid level in the reservoir drops too low, sensors may trigger the warning light. This can be caused by worn brake pads (which require more fluid in the calipers) or a leak in the lines.
3. Broken Tone Rings
The tone ring is a toothed metal ring located on the wheel hub or axle. The speed sensor reads these teeth to determine wheel speed. If a tooth is chipped, missing, or clogged with debris, the sensor signal becomes erratic, triggering the light.
4. Wiring Harness Damage
Because wheel speed sensors are located in the wheel wells, the wiring connecting them to the chassis is exposed to road debris, salt, ice, and suspension movement. Corroded wires or loose connections are a very common source of ABS faults.
Scanning ABS Error Codes and Diagnostics
Diagnosing an ABS light is not a guessing game; it requires digital intervention. Unlike older mechanical issues where you might listen for a sound, modern ABS diagnostics rely on the On-Board Diagnostics (OBDII) system.
To pinpoint the issue, you or a technician must use an OBDII scanner that is specifically capable of reading ABS/SRS codes. Note: Basic engine code readers often cannot access the ABS module. You need a scanner with specific ABS protocol support.
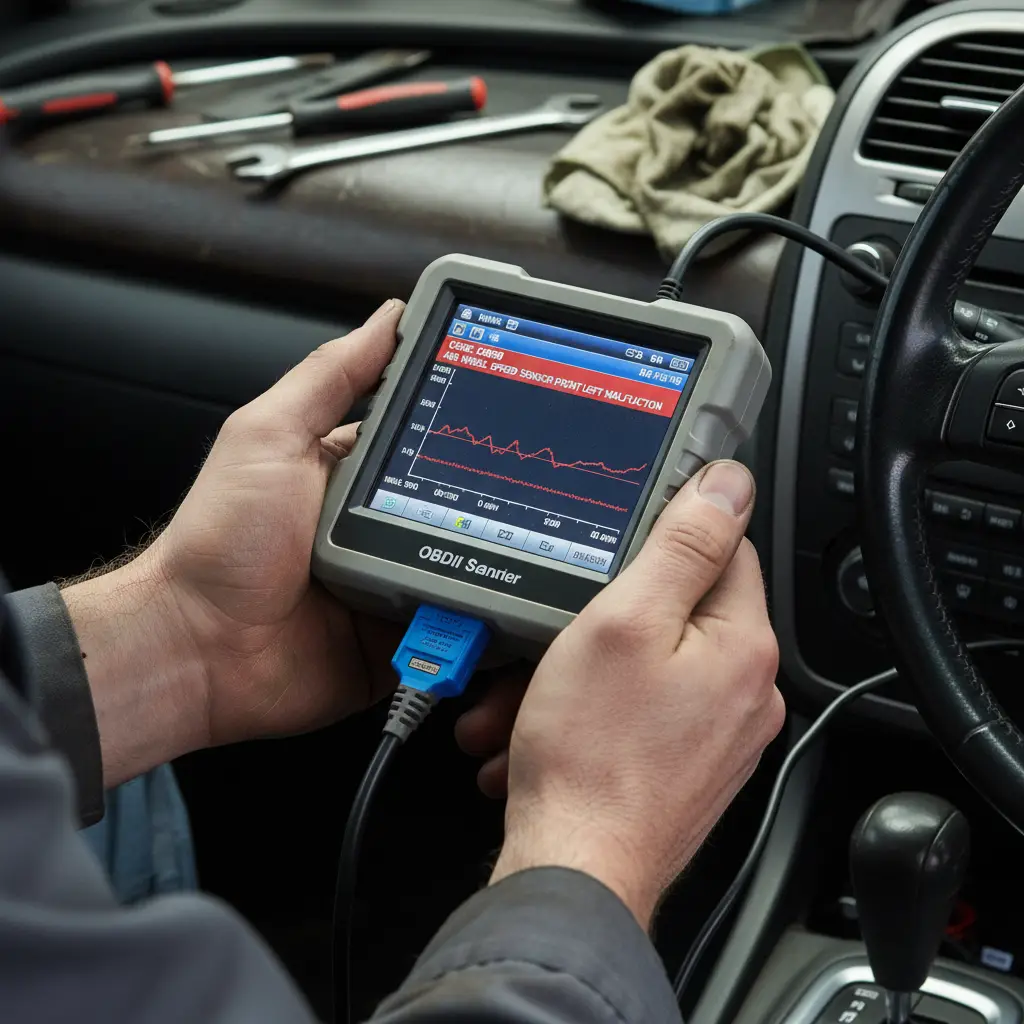

Once the scanner is connected, it will query the ABS control module. The module will return a specific Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC), such as:
- C0035: Left Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0040:00: Right Front Wheel Speed Sensor Circuit Malfunction.
- C0110: Pump Motor Circuit Malfunction.
These codes provide a roadmap. For instance, if the code points to the “Left Front Sensor,” you can stop inspecting the rear brakes and focus your attention entirely on that specific corner of the vehicle.
Wheel Speed Sensor Faults: The #1 Culprit
In the vast majority of cases where the abs light on car dashboards appears, the wheel speed sensor is to blame. These sensors are subjected to the harshest environment of any electronic component on a vehicle. They endure extreme heat from the brakes, vibration from the road, and constant exposure to water, mud, and snow.
How They Fail
Most sensors are magnetic. Over time, they can accumulate metallic dust from the brake rotors (brake dust). This metallic buildup interferes with the magnetic field the sensor uses to count the rotation of the tone ring. Cleaning the sensor with a rag and some brake cleaner can sometimes resolve the issue.
However, internal failure is also common. The internal copper windings can break due to vibration, creating an “open circuit.” When this happens, the sensor stops sending a signal entirely. A technician can verify this by using a multimeter to check the resistance (Ohms) of the sensor or by viewing “live data” on a scanner while spinning the wheel. If the wheel spins but the graph shows 0 MPH, the sensor is dead.
For more technical details on vehicle safety systems and sensor technologies, reliable resources like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) provide in-depth engineering reports and safety standards.
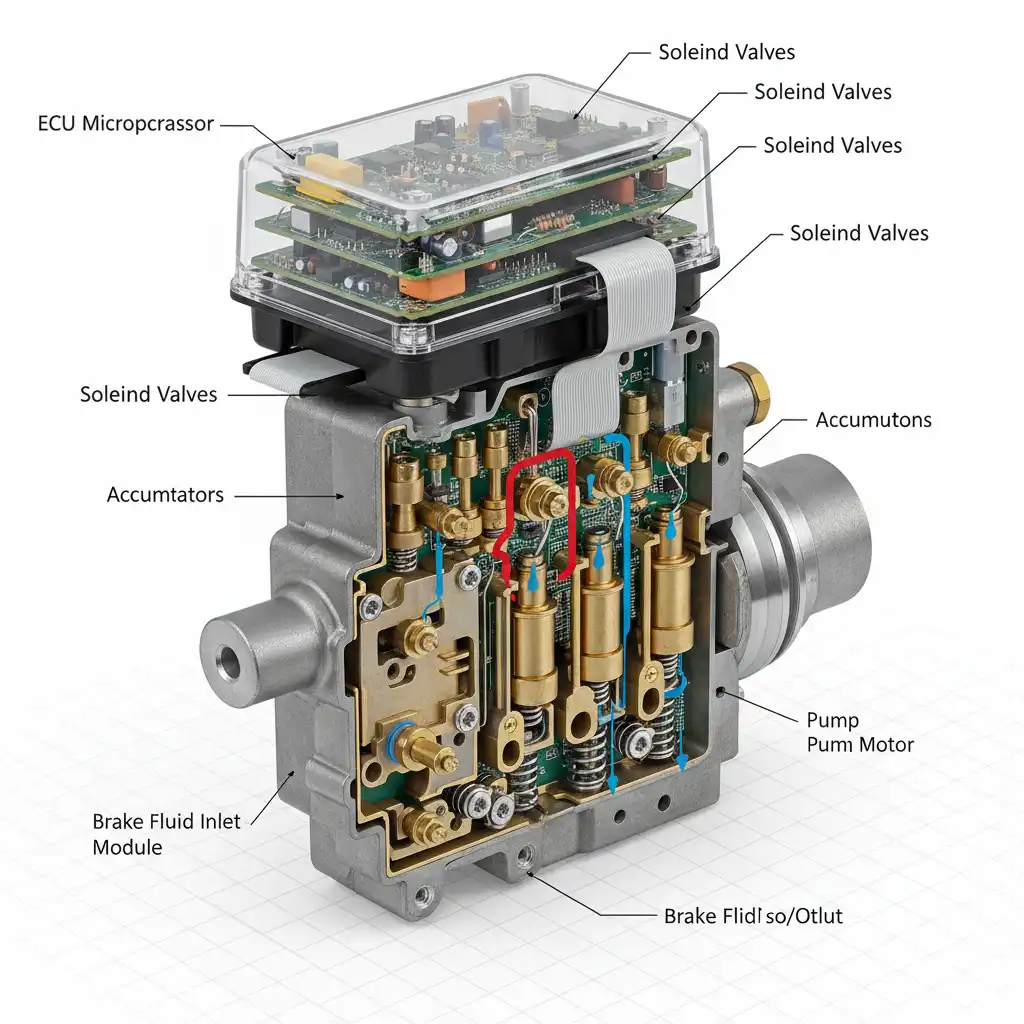
ABS Module and Hydraulic Pump Issues
If the sensors verify as functional, the diagnosis moves upstream to the ABS Control Module and the hydraulic pump assembly. This is the “brain” and “muscle” of the system.
The ABS module is a computer that processes sensor data. The pump is a mechanical device that physically moves brake fluid to modulate pressure. In many modern cars, these are combined into a single unit. Failures here are often caused by:
- Cold Solder Joints: Over years of thermal cycling (heating up and cooling down), the solder points on the circuit board inside the module can crack, breaking the electrical connection.
- Stuck Valves: Old, contaminated brake fluid can cause the tiny valves inside the hydraulic block to seize.
- Pump Motor Failure: The electric motor that drives the pump can simply wear out over time.
Replacing an ABS module is significantly more expensive than replacing a sensor. It often requires programming the new module to the vehicle’s VIN using factory-level software. However, there is a thriving market for remanufactured modules, which can save vehicle owners hundreds of dollars compared to buying a new unit from the dealership.
DIY Fixes vs. Professional Repair
Can you fix the ABS light yourself? It depends on the root cause and your skill level.
DIY-Friendly Tasks
- Checking Fuses: Anyone can check the fuse box diagram and swap a blown ABS fuse.
- Checking Fluid: Topping off the brake fluid reservoir is a standard maintenance task.
- Replacing Speed Sensors: On many vehicles, replacing a speed sensor involves removing the wheel and one bolt holding the sensor in place. It is a moderate-difficulty job accessible to most DIYers with a jack and basic hand tools.
Professional Required Tasks
- Module Replacement: Due to the need for software coding and bleeding the ABS hydraulic block (which requires a scanner to cycle the valves), module replacement is best left to professionals.
- Electrical Tracing: Finding a break in a wiring harness buried deep within the chassis requires patience, schematics, and electrical testing expertise.
Ignoring the light is not a strategy. While the car may drive, the liability and safety risk increase with every mile. According to Wikipedia’s overview of ABS history and function, these systems have been instrumental in reducing crash severity for decades. Ensuring yours is operational is a critical aspect of responsible vehicle ownership.
People Also Ask
Can I drive my car if the ABS light is on?
Yes, you can generally drive your car with the ABS light on, as the standard hydraulic braking system will still function. However, the anti-lock safety feature will be disabled. This means you should drive with extra caution, especially in wet or slippery conditions, as your wheels could lock up during a panic stop.
How do I reset the ABS light on my car?
The ABS light cannot usually be reset simply by disconnecting the battery. The system runs a self-check every time you start the car; if the underlying problem (like a bad sensor) persists, the light will come back on immediately. To reset it permanently, you must fix the fault and then clear the code using an OBDII scanner capable of reading ABS systems.
What is the most common cause of an ABS light?
The most common cause is a faulty wheel speed sensor. These sensors are located at each wheel hub and are exposed to road debris, water, and heat, making them prone to damage or becoming clogged with metal shavings and brake dust.
How much does it cost to fix an ABS light issue?
The cost varies wildly depending on the cause. A wheel speed sensor replacement typically costs between $100 and $250. However, if the ABS control module or pump has failed, repair costs can range from $600 to over $1,200 depending on the vehicle make and model.
Will an ABS light cause a failed state inspection?
In many jurisdictions, an illuminated ABS light is grounds for failing a safety inspection. Inspectors view the ABS as a critical safety component; if the warning light is on, the system is considered non-functional, and the vehicle is deemed unsafe for certification.
Can low brake fluid cause the ABS light to come on?
Yes, low brake fluid is a common trigger. The ABS system relies on hydraulic fluid pressure. If the reservoir level drops below a certain point, sensors will alert the system, often triggering both the ABS light and the red brake warning light.
